ALIGNMENT

A wheel alignment consists of adjusting your vehicle’s wheels so that all wheels are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the ground. Three basic angles contribute to proper wheel alignment: camber, caster, and toe. Camber is the measure of the degree of perpendicular offset from the road surface. Caster is the angle of your wheel’s pivot, which is attached to the suspension, and when this angle is out of alignment, straight-line tracking is affected. Toe refers to the angle of directional difference between the tire and the centerline of the vehicle. The front and rear wheels on your vehicle should always be perpendicular to the ground and parallel to the tire beside it. Routine wheel alignments have the potential to save you money in the long run while promoting optimal vehicle performance.
WHAT IS TIRE ALIGNMENT?
Alignment refers to an adjustment of a vehicle’s suspension – the system that connects a vehicle to its wheels. It is not an adjustment of the tires or wheels themselves. The key to proper alignment is adjusting the tires’ angles, which affects how they make contact with the road.
HOW DO I KNOW IF I NEED A TIRE ALIGNMENT?
There are a couple of ways to tell if your car needs a tire alignment. If you’ve noticed one or more of these indicators, you should have your alignment checked by a licensed service technician immediately.
- Uneven tread wear
- Vehicle pulling to the left or right
- Your steering wheel is o-center when driving straight
- Steering wheel vibration
CAMBER, TOE, & CASTER
When a technician checks your tire alignment, he or she is mainly concerned with three things:
1.CAMBER
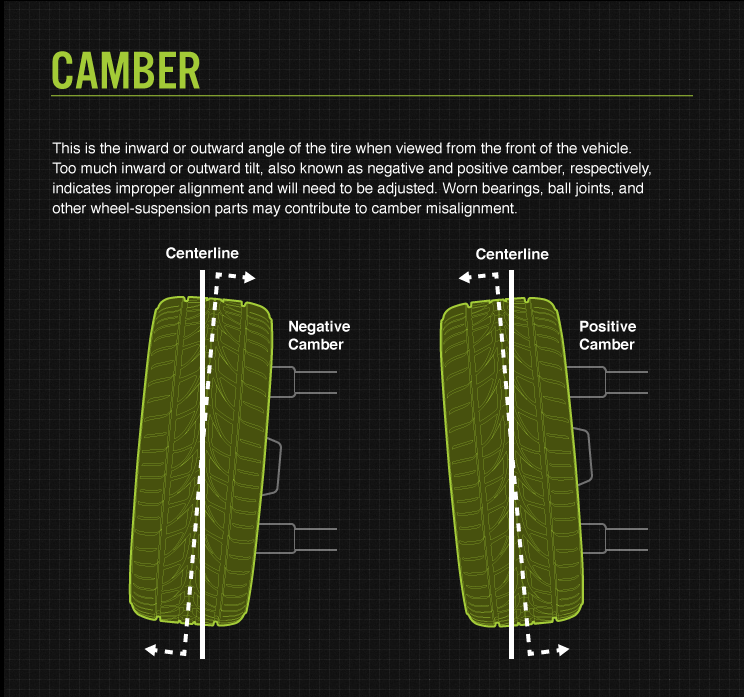
This is the inward or outward angle of the tire when viewed from the front of the vehicle. Too much inward or outward tilt, also known as negative and positive camber, indicates improper alignment and needs to be adjusted. Worn bearings, ball joints, and other wheel-suspension parts may contribute to camber misalignment.
2.TOE
Distinct from camber alignment, toe alignment is the extent to which your tires turn inward or outward when viewed from above. If that’s confusing, stand up and look down at your feet. Angle them inward toward the center of your body. When the tires on your car are angled the same way (remember, we’re thinking in terms of birds-eye-view), we call this toe-in alignment. Angle your feet outward, and you have toe-out alignment. Both require adjustment.

3.CASTER
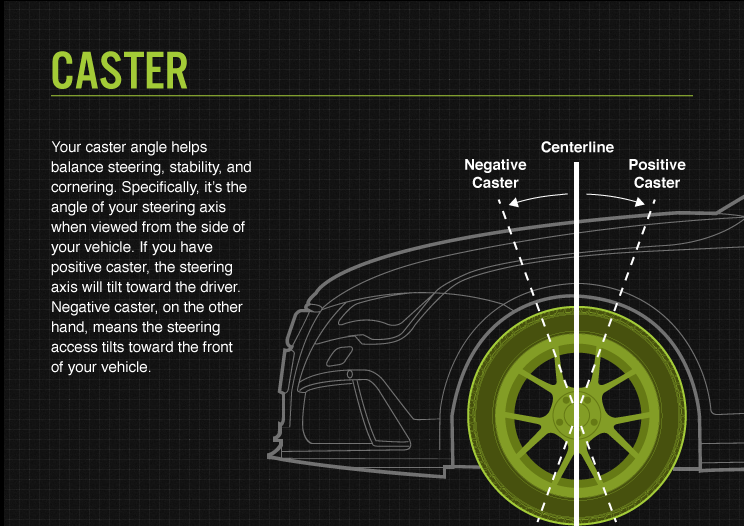
Your caster angle helps balance steering, stability, and cornering. Specifically, it’s the angle of your steering axis when viewed from the side of your vehicle. If you have a positive caster, the steering axis will tilt toward the driver. On the other hand, a negative caster means the steering axis tilts toward the front of your vehicle.
WHY TIRE ALIGNMENT MATTERS
Improper wheel or tire alignment can cause your tires to wear unevenly and prematurely. Here are some specific types of undue tread wear attributable to misalignment:
FEATHERING
Tires are “feathered” when the tread is smooth on one side and sharp on another. This is usually a sign of poor toe alignment.
CAMBER WEAR
This strain of tread wear means the inside or outside of the tread is significantly more worn than the tread center. As its name implies, positive or negative camber causes this type of wear.
HEEL/TOE WEAR
This happens when one side of your tread blocks wears down more quickly than the other in a circumferential direction. When you run your hand over the tread, it will look and feel like saw teeth when viewed from the side. Heel/toe wear could be a sign of under inflation and/or lack of rotation.
If you’re experiencing any of these unusual wear patterns, you should have a technician check your alignment. While tire wear prevention is a good reason to keep your wheel alignment in check, the consequences of misalignment can also play out in overall vehicle performance. A car that pulls to one side or steers erratically, for example, probably has an alignment problem.
TIRE BALANCING
Distinct from tire alignment, tire, or wheel balancing refers to compensation for any weight imbalances in the tire/wheel combination and is often performed in conjunction with a wheel alignment. Two basic types of tire/wheel imbalance need correction – static (single plane) and dynamic (dual plane).
Static balance addresses balance on only one plane – vertical movement, which can cause vibration. On the other hand, a dynamic imbalance addresses balance in two planes – vertical movement and lateral movement. Both types of imbalance require the use of a special balancing machine to help even things out.
To begin balancing your tires, a technician will mount them on the correct rims and adjust the pressure to optimal inflation. Then each tire goes on the center bore of a balancing machine. The machine spins the tire at high speed to measure the wheel/tire combination imbalance. It signals how much weight the tech should add to balance out the tire and the areas where said weight is needed.
Tire balancing is essential for proper tire care for the same reason as wheel alignment: prevention of premature tread wear. Having tires balanced every 5,000 to 6,000 miles can help maximize their lifespan and overall performance.
